————
Information and pictures on Scabies, a common sexually transmitted disease. Information including symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, transmission, prevention and other general information.
———–
The scabies mite has infested humans for at least 2,500 years. More than 300 million cases of scabies occur worldwide every year. Anyone of any race or age, regardless of personal hygiene can be affected.
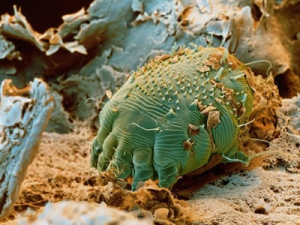
Scabies is a contagious, itchy skin condition caused by very small, wingless arthropods called the Human Itch mite or Scabies itch mite Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis (Hering). These tiny arthropods are not insects and have eight legs like spiders. They are just visible to the eye (about 0.4mm) and have round bodies.
Scabies Cycle
Attracted to warmth and odor, the female mite is drawn to a new host, making a burrow, laying eggs and producing secretions that cause an allergic reaction. Larvae hatch from the eggs and travel to the skin surface, lying in shallow pockets where they will produce secretions.
The female insect burrows into the skin where she lays 1-3 eggs daily. If untreated, the female will continue to lay eggs for about 5 weeks. The eggs hatch and the new mites begin the cycle all over again.
An allergic reaction to the mite, its eggs and feces occurs, which irritates and inflames skin. The rash is extremely itchy, which often causes sleeping problems especially in infants and young children.
Scabies Symptoms
A very small, hard to see, zigzag blister usually marks the trail of the mite as she lays her eggs.
Other more obvious symptoms are:
- intense itching especially at night
- a red rash can occur at the area that has been scratched.
- skin may become crusty or scaly as the infection progresses
Early scabies rash will show up:
- little red bumps like hives
- pimples
- tiny bites
Scabies usually begins in the body’s folds and crevices, such as:
- armpits
- around the nipples for women
- beneath nails
- belt line
- between the fingers
- buttocks
- elbows
- inner thighs
- on the penis for men
- skin under rings, bracelets or watch bands
- wrists
Children usually have more overall itching on the
- palms of hands
- soles of feet
- scalp
The child may also have
- irritability
- sleeplessness
- tiredness
due to itching
In babies the neck and head may be affected
The itching is due to an allergic reaction to the tiny mites, which is associated with a rash of red, raised spots.
Bacterial infection may occur through infected lesions. In many cases, children are treated because of infected skin lesions rather than for the scabies itself.
————
Photos of Scabies Symptoms—————
Complications of Scabies
When large areas of the body, hands and feet are scaly and crusted, the disease is called crusted scabies where symptoms are far more severe than usual. These crusts hide thousands of live mites and eggs, making treatment difficult.
This type of scabies occurs mostly among the elderly and in AIDS patients.
———
Scabies Transmission
Scabies is very contagious and is usually spread by:
- close contact, usually starting at the wrist caused by holding hands with a person who has scabies.
- close contact with infected clothing, bedding or towels
- personal contact
- shaking hands
- sleeping together
Although the mite burrows under the skin the rash and itch are more widespread than just the locations of the mites.
Most common breeding environments are:
- in overcrowded living conditions
- in school children playing together
- families
- roommates
- sexual partners
- mothers of infants
- elderly people in nursing homes
- soldiers
- prisoners
The mite or the egg can spread the infection and the mite can survive on objects for a long time, so constant washing of clothing, towels or bedding is necessary.
Scabies does not occur because of poor hygiene.
Scabies Diagnosis
Because the scabies rash looks like other itchy conditions, such as eczema, scabies can be difficult to diagnose unless more than one family member also has an itchy rash.
Microscope Test
The most common test involves the suspected area being mixed with sterile mineral oil and the scrapings viewed under a microscope to detect scabies mites, eggs and/or feces.
Ink Test
An ink test is where a blue or black felt-tipped pen is applied to the suspected areas. After the skin is cleaned mite burrows can be located if the ink sinks into them.
Scabies Treatment
Prompt action is required as scabies is very hard to eradicate once infected.
Currently three main types of solutions are used for scabies. All are applied to the whole body except the head and neck, and all whole family should be treated.
Permethrin
- used because of its relative safety and low irritant quality
- is safe for use on the head and neck of children less than two years old.
Benzyl benzoate emulsion
- is washed off after 24 hours and repeated 2 or 3 times
- has to be diluted in 2 to 3 times more water in infants or young children the solution to help reduce skin irritation
Malathion
- is washed off after 24 hours
- kills the mites but their bodies remain in the skin causing the itch to persist until our own natural defense systems break down and remove what is left of the mites which takes about 2 weeks
- the itch continues for about 2 weeks after the treatment
If using a prescribed (poison) lotion, follow the instructions very carefully.
Sulfur
- has been used since Roman times (6-10% in lotion or cream)
- some people have an allergic reaction
For young children with scabies:
A medicated cream such as Elimite (a prescription medication) can be used to treat the infection.
Method
- apply a thin layer of cream from the neck down avoiding the face and scalp before going to bed
- the cream should be applied between the fingers and toes and beneath the tips of the fingernails (the eggs may be under the nails due to scratching)
- wash off with soap and water 8-12 hours later
Caution
Call your doctor if your child shows signs of:
- fever
- pus drainage
- red streaks on the skin
- red, swollen, warm areas
- skin infection
Help Factors
- a sauna
- keep fingernails cut short and apply mitts or socks to infants’ hands at bedtime to cut down on scratching.
Bathing, washing or soaking in diluted:
- borax
- enzyme cleaners
- lice shampoo
- sulfur
Do not treat scabies with:
- hard soaps
- home remedies
- kerosene
- laundry detergent
Consult a dermatologist before using steroids or any other creams.
Scabies Prevention
- avoid sharing personal articles such as clothing, hair brushes, combs or towels
- check family members
- chemical sprays for the household are unnecessary
- clothes, towels, bedding, combs, brushes, and anything else the person has had contact with should be soaked in very hot water in enzymes or borax for 15 minutes or more
- clothing and underwear should be changed regularly
- have regular saunas
- if your child has scabies, please notify the school authorities
- keep all bedding well laundered (hot water, 120oF)
- practice proper prevention measures
- vacuum rugs and furniture, such as chairs and couches, that the infected person might have been in contact with.
For more information on Scabies, watch this video: