————
Information and pictures on Trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted disease. Information including symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, transmission, prevention and other general information.
——-
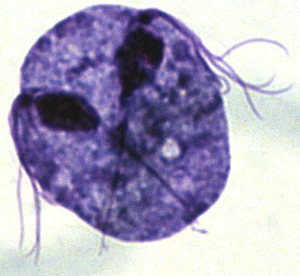
Trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted disease caused by a single-cell parasitic protozoan, Trichomonas vaginalis, which was first discovered in 1836. T vaginalis has five distinctive hair-like flagella which are used to move the cell around.
About 5 million Americans develop trichomoniasis every year. It has been found in:
- 5%-15% of women at gynecology clinics
- 50%-75% of prostitutes in the United States
It is often diagnosed in patients who are already infected with other STDs such as:
- gonorrhea
- nongonococcal urethritis (NGU)
——
Contents
Trichomoniasis Symptoms
Trichomoniasis infection frequently has no symptoms. There have been rare cases where the incubation period of the infection has covered years, but usually symptoms appear within 4-20 days of exposure, and include:
In women
- blood spotting in vaginal discharge
- heavy, yellowish-green or gray, frothy vaginal discharge
- infection in the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body
- itching, burning or pain in the vagina
- lower abdominal pain
- musty vaginal odor
- pain and/or burning when urinating
- pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
- swelling in the groin
- swollen and irritated vagina and cervix
- urinating more than usual
- vaginal or vulval redness
- worsening symptoms when menstruating
In Men
Men rarely have any symptoms, however, if symptoms do occur they include:
- infection of the urethra or prostate gland, which is involved in semen production
- painful and/or difficult urination
- thin, whitish discharge from the penis
- tingling inside the penis
* Men mostly do not show symptoms but it is advisable to seek treatment if their partner has Trichomoniasis as infection is likely.
———-
Photos of Trichomoniasis Symptoms
——–
Trichomoniasis Transmission
The parasite rarely causes symptoms in men and re-infection of women by untreated partners can often occur.
It can be spread during:
- anal sex
- mutual masturbation when bodily fluids from one partner come in contact with the other’s genitals (in rare cases)
- oral sex
- vaginal sex
Unlike most STDs, Trichomonas can survive for some hours outside the body on infected objects and can be transmitted by sharing:
- bodily fluids
- contaminated bedding
- damp towels
- sheets
- toilet seats
————
Trichomoniasis Diagnosis
Trichomonas is a pear-shaped protozoan with 5 hair-like ‘tails’ called flagella (four anterior and one posterior). Protozoans are single celled animals that have a nucleus in their cells. This distinguishes them from bacteria, which have a cellular structure but no nucleus. Flagellate protozoa like T. vaginalis use their flagellae to move the cell around. The presence of the five flagellae and the jerky movements of the cells, when seen through a microscope, are distinctive and assist in its identification.
Trichomoniasis Diagnosis can be made by:
Culture Tests
A culture of the organism or an antibody test may be done, especially in men, as relatively few of the parasites are found in discharges from the penis.
Examination under a Microscope
Samples of vaginal discharge or secretions from the penis are examined under a microscope.
Laboratory Testing
Samples of vaginal discharge or secretions from the penis may be sent to a laboratory to see if Trichomonas is present and may take up to 2 weeks for the results.
Pap smears
Pap Smears are sometimes used to confirm diagnosis.
———
Trichomoniasis Treatment
Antibiotics are usually successful (cure rate 95%) even though this infection is not a bacteria. It is usually administered in a single dose.
Procedure
Sexual partners need treatment at the same time to eliminate the parasite and to prevent re-exposure and re-infection.
Antibiotics used are:
Metronidazole
This antibiotic is also called Flagyl
Caution
If taken with alcohol it can cause severe:
- nausea
- vomiting
Azithromycin
This antibiotic is also called Zithromax and has fewer side effects but is more expensiv
5-notroimidazoles
These drugs are successful for both partners.
If left untreated Trichomoniasis can:
- be spread to your sexual partner(s)
- cause infections in the urethra or prostate gland in men
- continue to cause uncomfortable symptoms
———
Trichomoniasis Prevention
Transmission of this parasite from one person to the next may be reduced by:
- abstinence from sex until the infection is cured
- consistent and correct latex condom use, put on before starting sex and worn until the penis is withdrawn
- spermicides and diaphragms may provide some protection
- treatment of the male partner as well as the female
Help Factors
- if you come in contact with trichomoniasis see your doctor, health professional or urologist immediately
- know your partner’s sexual history
- limit one’s sexual relationship to a single, uninfected partner
Note
- douching or urinating after sex does not prevent STDs
- frequent use of spermicides can cause vaginal inflammation
———–
Trichomoniasis Prognosis
It has been shown that Trichomoniasis:
- is associated with increased risk of transmission of HIV.
- may cause a woman to deliver a low-birth-weight or premature infant.